Services
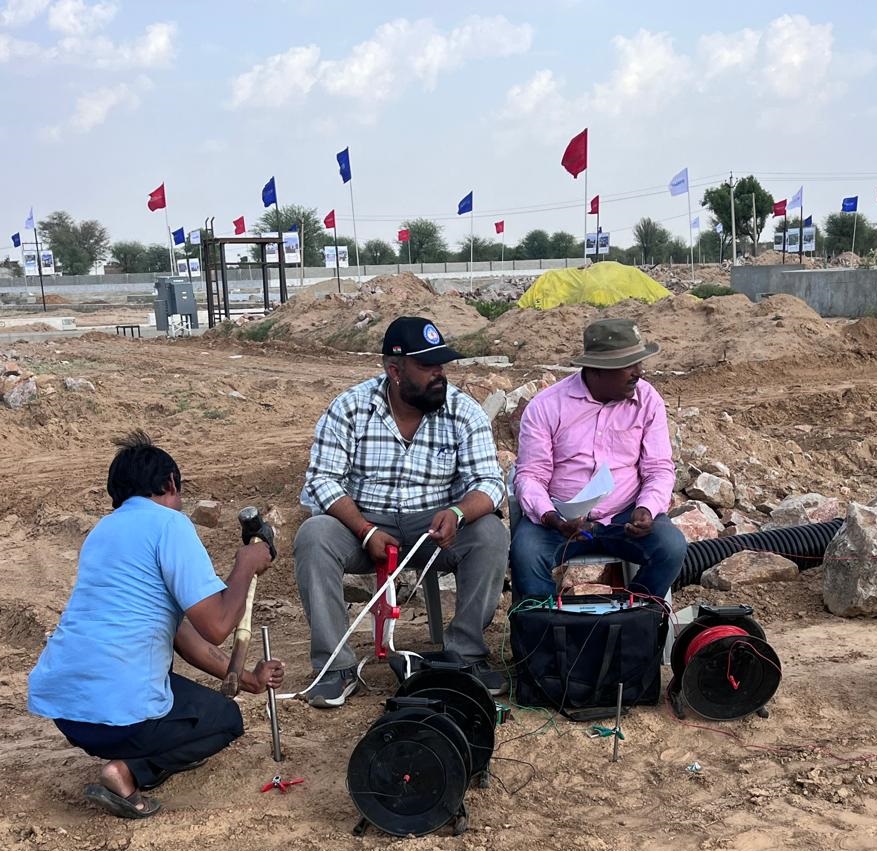
Geological Survey
Geological Survey is a systematic study and mapping of the Earth’s structure, composition, and natural resources. It involves collecting data on rocks, minerals, groundwater, soils, and landforms to understand geological processes and support activities such as mining, construction, water management, and disaster mitigation. National agencies like the Geological Survey of India (GSI) or the US Geological Survey (USGS) conduct such surveys to provide scientific information for resource planning, environmental protection, and sustainable development.
Geological Survey Report provides a systematic record of field investigations, mapping, and subsurface studies conducted to analyze the Earth’s structure, lithology, mineral resources, groundwater potential, and geohazards. It includes data from drilling, sampling, geophysical methods, and laboratory analysis, presented with maps, cross-sections, and interpretations to support resource management, engineering projects, and environmental planning.

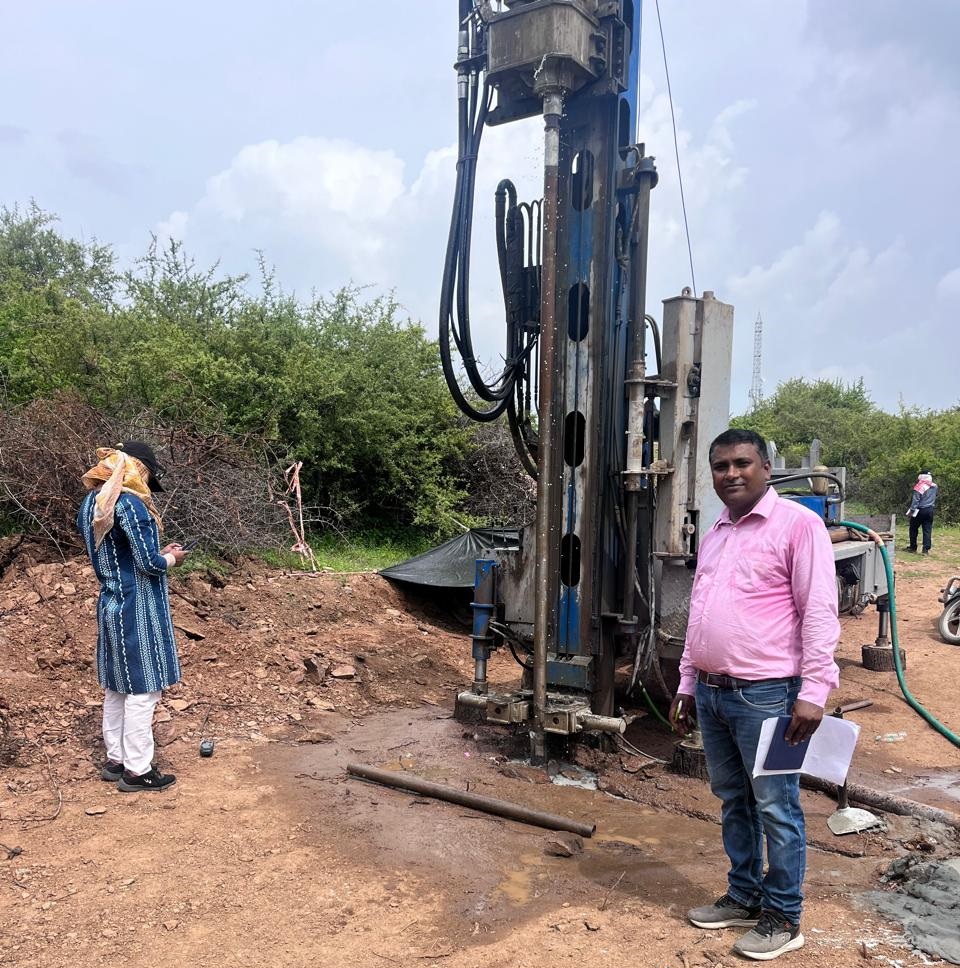
Drilling Services
Drilling Services involve specialized techniques and equipment used to drill into the earth for exploration, extraction, or construction purposes. They are widely applied in oil & gas, mining, groundwater exploration, and geotechnical investigations to access resources, collect samples, or create foundations.
Drilling Services Report documents the methodology, equipment, and results of drilling operations conducted for exploration, geotechnical, groundwater, or resource extraction purposes. It typically includes details on drilling techniques (rotary, percussion, core drilling), borehole logs, depth and lithology records, sampling procedures, groundwater levels, and core recovery. The report also provides analysis of subsurface conditions, encountered formations, and recommendations for construction, mining, water well development, or further geological investigation.

Water Testing Services
Water Testing is the analytical evaluation of water samples to determine their physical, chemical, and microbiological characteristics. It involves laboratory techniques such as spectrophotometry, chromatography, titration, and microbial culturing to detect parameters like pH, turbidity, dissolved oxygen, total dissolved solids (TDS), hardness, heavy metals, organic compounds, and pathogenic organisms. The results are compared with regulatory standards (e.g., BIS, WHO, EPA) to assess potability, industrial suitability, and environmental compliance.

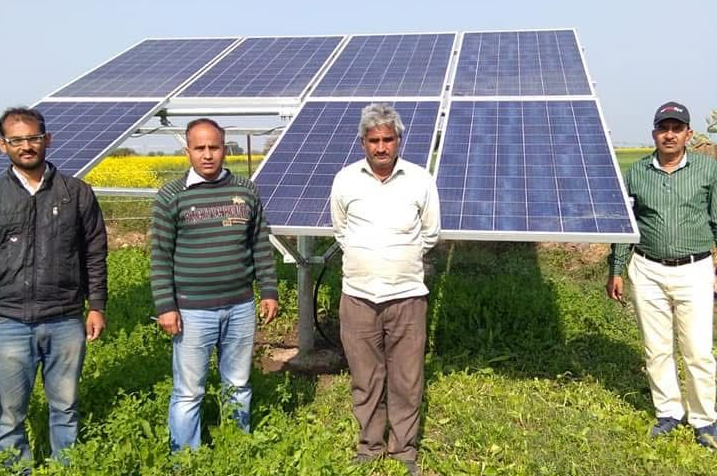
Solar Services
Solar Services encompass the engineering, procurement, installation, and lifecycle management of photovoltaic (PV) and solar thermal systems. Technical activities include site assessment using solar irradiance data, load analysis, system sizing, module mounting structure design, inverter and storage integration, grid interconnection, and compliance with electrical and safety codes (IEC, IEEE, NEC). Services also involve performance modeling (using tools like PVsyst), monitoring through SCADA/IoT platforms, preventive and corrective maintenance, and efficiency optimization to maximize energy yield and system reliability.

Mining - Environment clearance, Mining Plan
Mining – Environment Clearance (EC) is the statutory approval granted by regulatory authorities (such as the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change in India) that permits mining projects to operate after assessing their environmental impacts. The clearance process involves Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA), Environmental Management Plan (EMP), public consultation, and compliance with environmental laws related to air, water, land, biodiversity, and rehabilitation. Obtaining EC ensures that mining activities are carried out in a sustainable and legally compliant manner.
Mining Plan is a detailed document prepared to outline the systematic development and scientific exploitation of a mineral deposit. It includes geological studies, reserve estimation, method of mining, machinery deployment, drilling and blasting techniques, production scheduling, safety measures, environmental management, reclamation, and closure plans. Approved by regulatory authorities (such as IBM in India), the mining plan ensures resource conservation, operational efficiency, worker safety, and environmental sustainability throughout the mine’s lifecycle.